
The Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence team presented a new study that reveals ransomware as the most widespread Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) over the past seven years. The study is based on research conducted on 97 malware families that have been distributed on the darknet and other resources. Additionally, the researchers found that cybercriminals often lease infostealers, botnets, loaders, and backdoors to carry out their attacks.
MaaS is an illicit model of business involving the leasing of software to carry out cyberattacks. Typically, clients of such services are offered a personal account through which they can control the attack, as well as technical support. It lowers the initial threshold of expertise needed by would-be cybercriminals.
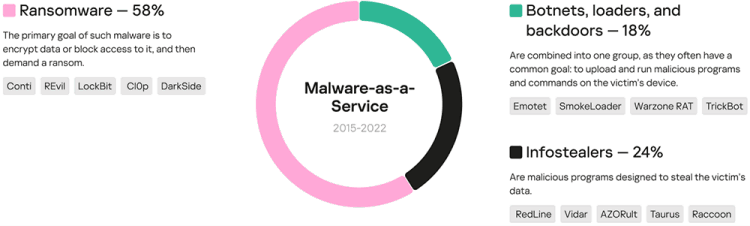
Ransomware the most popular MaaS
Kaspersky examined various malware families’ sale volumes, as well as mentions, discussions, posts, and search ads on the darknet and other resources regarding MaaS to identify the most popular types. The leader turned out to be ransomware, or malicious software that encrypts data and demands payment for decryption (IoT botnets are not included since they are not distributed under the MaaS model, but DDoS-as-a-Service model). It accounted for 58% of all families distributed under the MaaS model between 2015 and 2022. The popularity of ransomware can be attributed to its ability to generate higher profits in a shorter space of time than other types of malware.
Cybercriminals can ‘subscribe’ to Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) for free. Once they become partners in the programme, they pay for the service after the attack happens. The payment amount is determined by a percentage of the ransom paid by the victim, typically ranging from 10% to 40% of each transaction. However, entering the programme is no simple task, as it entails meeting rigorous requirements.
Infostealers accounted for 24% of malware families distributed as a service over the analysed period. These are malicious programs designed to steal data such as credentials, passwords, banking cards and accounts, browser history, crypto wallets data, and more.
Infostealer services are paid through a subscription model. They are priced between $100 and $300 per month. For example, Raccoon Stealer, which was discontinued in early February 2023, could be acquired for $275 per month or $150 per week. Its competitor, RedLine, has a monthly price of $150, and there is also an option to purchase a lifetime license for $900, according to the information posted on the darknet by its operators. Attackers also make use of additional services for extra pay.
Furthermore, 18% of malware families being sold as a service proved to be botnets, loaders, and backdoors. These threats are combined into one group since they often have a common goal; to upload and run other malware on the victim’s device.
“For instance, the price of loader Matanbuchus tends to vary over time. The price in June of the current year starts from $4900 per month. This type of malware is more expensive than infostealers, for example, as the malicious code itself is more complex and the operator provides all the infrastructure in this case – meaning the partners don't have to pay extra for bulletproof hosting services. It is also worth noting that the number of subscribers to Matanbuchus is very limited, allowing attackers to remain undetected for a longer time,” said Alexander Zabrovsky, Digital Footprint Analyst at Kaspersky.
Components of MaaS and malefactor hierarchy
The cybercriminals who operate MaaS platforms are commonly referred to as operators, whereas those who purchase these services are known as affiliates. After closing a deal with operators, affiliates receive access to all necessary components of MaaS, such as command-and-control (C2) panels, builders (programs for quick creation of unique malware samples), malware and interface upgrades, support, instructions, and hosting. The panels are an essential component allowing attackers to control and coordinate the activities of the infected machines. For example, cybercriminals are able to exfiltrate data, negotiate with a victim, contact support, create unique malware samples, and much more.
Some types of MaaS, such as infostealers, allow affiliates to create their own kind of team. Members of such a team are called traffers – cybercriminals who distribute malware to increase profits and generate interest, bonuses, and other payments from affiliates. Traffers do not have access to C2 panel or other tools. Their only purpose is to scale up the spread of the malware. Most often, they achieve this by disguising samples as cracks and instructions for hacking legitimate programs on YouTube and other websites.
“Cybercriminals actively trade illicit goods and services, including malware and stolen data, over the shadow segments of the Internet. By understanding how this market is structured, companies can gain insights into the methods and motivations of potential attackers. Armed with this information, we are able to better help businesses develop more effective strategies that prevent cyberattacks by identifying and monitoring cybercriminal activities, tracking the flow of information, and staying up to date on emerging threats and trends,” added Zabrovsky.
Find out more at www.kaspersky.co.za

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.