

We all know that cybersecurity is important. It’s mentioned in the national news on almost a daily basis, whether it is about government vulnerabilities, cyberterrorism, or major retailers being targeted by criminals, resulting in millions of customers’ credit card details being stolen. But, like securing physical spaces, it’s one of those things that only becomes newsworthy when it fails.

For a long time, physical security was strictly analogue, and it’s only connection to the IT network was at its end-point. And therefore, those responsible for physical security didn’t need to concern themselves with network security, while at the same time, the IT department didn’t need to be concerned with any undue exposure from cameras, etc.
Sure, hacks have always occurred even in analogue systems (the prototypical breach through a baby monitor or garage door opener being well known examples). But now that IP-based security systems are becoming the norm with all the associated benefits, both sides need to be aware that the game has changed.
The challenge, as we see it, is that the physical security team and the IT team have, on the face of it, very different outlooks and priorities, and often don’t really understand each other. Physical security is from Mars and the IT department is from Venus.
Often it can simply be a language/jargon barrier, where neither side truly ‘gets’ what the other one is talking about. But in many cases, it can also be more akin to a border dispute, or a custody battle for an unwanted child – the physical security team doesn’t consider cybersecurity to be part of their job, and the IT department may not even be aware of the potential vulnerabilities from a variety of devices that appear to have no obvious users or owners.
“Not my job”
One phrase stuck in my head after a recent conversation about cybersecurity with a customer: “We are not the Pentagon.” Basically, “we are glad Axis is thinking about this stuff, and it’s interesting, but we are pretty relaxed about it right now.” And if they haven’t been attacked (or at least don’t know if they have been attacked), then that response is often followed by “Cybersecurity is something that the IT department is worried about – I just have to make sure this building is secure.”
At the same time, when I have talked to the IT department, they have sometimes been unaware of the potential exposure of unsecured IP cameras.
So, how do we as an industry get the physical security manager to take IT security seriously? And conversely, how do we enable the IT security team to talk to their physical security colleagues in a language that they understand? Actually, it’s not that complicated. The best way is to use the terminology that they are both familiar with: (See table).
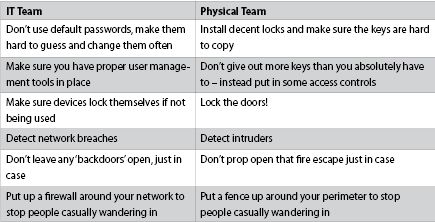
However, not all organisations and businesses are the same, and some already have effective communication between these two departments, and a good awareness of the threats they need to tackle together. What I have seen is that organisations tend to fit into one of three broad categories depending on their understanding of the threat they face.
At the top are those whose brand, business or credibility is based around trust and security – for example banks. By and large, they place security very high up their list of priorities, be it physical or computer-related, and it is ingrained within their corporate culture. They are often cautious about embracing new technologies until they can be sure their security won’t be compromised. This is especially true of new devices being connected to their network, such as cameras, access control points, etc. So their IT departments are highly unlikely to allow any new IP-based equipment to be connected, without ensuring they have been properly sourced, tested and set up.
Next, there are those who are aware that they may be vulnerable to cyberattacks, but may not have the specific expertise in-house to properly analyse their risks or to mitigate them. However, they are at least willing to get advice, even if it’s not a critical priority for them. These companies probably are the most at risk – with enough complexity in their networks to make management a full-time job, but possibly without sufficient resources to properly police every device that gets connected.
Lastly, there are those, usually smaller businesses, which have very little understanding of cybersecurity at all, and even less idea that devices such as cameras need to be properly secured before being connected to a network. They rarely have a full-time IT manager, let alone a person with sole responsibility for physical security. For these businesses, a very simple, automated set-up is ideal, with all security being taken care of out of the box.
In the end, though, both the IT and physical security departments need to care about the problem enough to want to engage with each other, and not just pass the buck back and forth until an attack actually happens. So, how to do that? Unfortunately, the case has already been made for us on several recent occasions.
Reality, not future problems
It was only a few months ago that the Mirai BotNet attack demonstrated how vulnerable IoT devices can be, how ubiquitous they are, and how these two facts make for a highly attractive opportunity for hackers. Over several months, cybercriminals infected millions of devices, including IP cameras, DVRs, home routers, etc. Then, in September 2016, it was first used to run a massive DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack on the website of a prominent security journalist, KrebsOnSecurity.com. A month later, it was followed by the largest DDoS attack in history, going after Dyn.com, one of the key parts of the US Internet backbone, upon which services such as Netflix, Spotify and Amazon rely.
Now, some may say that not being able to watch the latest episode of Orange is the New Black may not be a huge threat to Western civilisation, but this just goes to show the potential of what can be done with physical security devices that haven’t been properly hardened against cyberattack. The majority of the devices that were infected had easy-to-guess default passwords that had never been changed, or even worse, could not be changed at all. Or there were the devices that had ‘backdoors’ built into them to make it easier for the manufacturer to debug them during development, and were never closed again before production.
In December 2016, 80+ cameras from a major manufacturer were found to have backdoor accounts. A month later, it was reported in the Washington Post that for three days the Washington DC Police were unable to record video from their security cameras due to 70% of their storage devices being hacked.
We know that this won’t be the last time. The Internet of Things is currently an easy target, and even more so because there are very few human beings in the loop, so there is almost no-one to notice when an attack has occurred until too late. As the Mirai BotNet attack showed, an attack might not even directly affect the host, so there is even less chance of spotting an infection unless you are paying close attention.
For more information contact Axis Communications, +27 (0)11 548 6780, sasha.bonheim@axis.com, www.axis.com
| Tel: | +27 11 548 6780 |
| Email: | marcel.bruyns@axis.com |
| www: | www.axis.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Axis Communications SA |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.