
Kaspersky has found that 37% of computers – servers and workstations – used to collect, process and store biometric data (such as fingerprints, hand geometry, face, voice and iris templates), on which Kaspersky products are installed, faced at least one attempt of malware infection in Q3 2019.
Overall, a significant number of conventional malware samples were blocked, including remote-access Trojans (5,4%), malware used in phishing attacks (5,1%), ransomware (1,9%), and Trojan bankers (1,5%). These and other findings came from the ‘Threats for biometric data processing and storage systems’ report, prepared by Kaspersky ICS CERT.
Biometric data is increasingly part of everyday life, augmenting and replacing traditional authentication methods, such as those based on logins and passwords. Biometry-based authentication is used to access government and commercial offices, industrial automation systems, corporate and personal laptops and mobile phones. However, like many other technologies that have lately been rapidly evolving, biometric authentication systems have proved to have significant generic drawbacks. The key shortcomings of biometric authentication technologies are usually caused by information security issues.
With that in mind, Kaspersky ICS CERT experts conducted research into cyber threats that targeted computers used to collect, process and store biometric data with Kaspersky products installed in the first nine months of 2019.
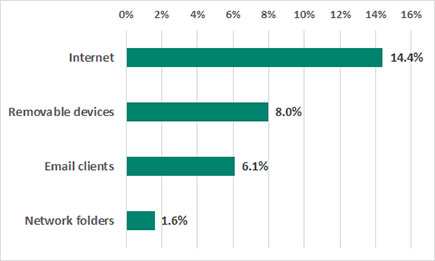
As it turned out, the products were triggered on 37% of such computers in the third quarter. An analysis of threat sources has shown that the Internet is the main source of threats for biometric data processing systems – threats with this source were blocked on 14,4% of all biometric data processing systems. This category includes threats blocked on malicious and phishing websites, along with Web-based email services.
Main sources of threats
Removable media (8%) are most often used to distribute worms. After infecting a computer, worms commonly download spyware and remote access Trojans as well as ransomware.
Threats blocked in email clients were ranked third (6,1%). In most cases these were typical phishing emails (fake messages on the delivery of goods and services, the payment of invoices, etc.) containing links to malicious websites or attached Office documents with embedded malicious code.
“Our research shows that the existing situation with biometric data security is critical and needs to be brought to the attention of industry and government regulators, the community of information security experts, and the general public. Though we believe our customers are cautious, we need to emphasise that infection caused by the malware we detected and prevented could have negatively affected the integrity and confidentiality of biometric processing systems. This is particularly the case for databases where biometric data is stored, if those systems were not protected,” said Kirill Kruglov, senior security expert, Kaspersky ICS CERT.
In order to stay protected from the potential risks of cyberattacks, Kaspersky experts advise:
• Minimise how exposed biometric systems are to the Internet and Internet-related threats. It is better if they are a part of an air-gapped infrastructure. Cybersecurity should be of the highest priority when new systems are designed and implemented.
• Make sure that the highest level of cybersecurity requirements are applied to the infrastructure that contain biometric systems, such as:
o Extensively training the operating personnel to resist possible cyberattacks.
o Ensuring all needed cybersecurity controls are in place.
o Enlisting a dedicated team of highly-skilled professional security experts that can keep track of the infrastructure security.
o Regularly conduct security audits to identify and eliminate possible vulnerabilities.
o Up-to-date strategic and tactical threat intelligence is constantly provided to the cybersecurity team.
See the report at https://ics-cert.kaspersky.com/reports/2019/12/02/biometric-data-processing-and-storage-system-threats/
| Tel: | +27 11 783 2424 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.kaspersky.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Kaspersky |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.