
Stafix considers the potential danger of ignorant or careless usage of perimeter electric fencing.
The introduction and proliferation of what was essentially an agricultural tool, the pulsed electric fence energiser used for animal control, into urban areas for the purposes of perimeter security, has necessitated a re-evaluation of certain safety aspects of this tool. When used in sparsely populated rural areas, the incidence of inadvertent human contact with electric fences is rare. However, since their effectiveness as a barrier against crime has been appreciated, they have become very popular in urban areas. The likelihood of inadvertent human contact with an electric security fence has therefore increased significantly.
Consider an example of an urban scenario where four houses share common boundaries and all are protected by electric security fences, as per the diagram. Assuming that the energisers installed comply with the stringent international safety standards, how then can this form of security fencing be dangerous? The answer lies in the possibility of a person making contact with more than one fence and receiving shocks from more than one energiser at the same time. This will increase the energy and/or frequency of the shock received. This, besides being illegal and contrary to international safety standards, could possibly cause injury to a person.
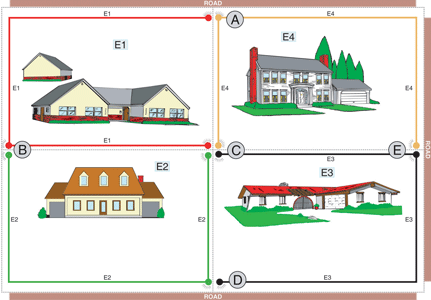
For example at points A,B,C,D, and E in the diagram, it is possible for an intruder or a member of the family for that matter, to make simultaneous contact with two different electric fences powered by two different energisers. And, should the four households independently fence all four sides of their properties, the possibility of unacceptably high power levels will also exist along the entire parallel sections of their common boundaries.
Despite the fact that each of the energisers installed at the respective households may be certified to the legal eight joule limit at 500 Ω, should it just so happen that they all pulse in perfect synchronisation with each other, a person making contact with the fences at any of the points A to E will receive the combined shock of two energisers. This could significantly increase the power level to exceed the current legal safety limit. There is also another more likely, and possibly more dangerous scenario: when the energisers are not pulsing in sync with each other. In this case the frequency between impulses could be so close that a person receives two shocks in such close proximity to each other that the fence becomes dangerous and illegal.
Legalities aside, what are the dangers to the person making contact with the fences? The first scenario could result in cardiac arrest and the second scenario, the more likely of the two, cardiac fibrillation. While the likelihood of either of these scenarios occurring is very slim, the industry needs to take cognisance of these possibilities in urban environments.
So what can be done about it? The answer is simple. Have all the energisers on the properties pulsing in perfect synchronisation with each other at legal pulse intervals, and with a combined energy output limited so as not to exceed eight joules. This is exactly what the new, internationally approved, JVA 14 and JVA 28 Security Electric Fence Energizers can be programmed to do and which makes them the ideal choice for security applications.
Finally, to ensure that the installation meets all existing legal standards and impending codes of practice, make sure that you have a copy of the current act and of the SANS 10222 9 (Draft 6) publication.
For more information contact Maurice Williamson, Stafix, +27 (0)82 557 2780, [email protected]
| Tel: | +27 11 397 3507 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.stafix.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Stafix |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.