
People’s constant need to interact makes them targets for all sorts of malicious software. This month’s top e-threats are distributed as follows: six Trojans, two worms, one exploit and one virus most of which to be found on torrents, 'warez' and other peer-to-peer platforms.
Trojan.Clicker.CM ranks first with 8,30% of the total amount of infected computers and is mostly found on file sharing websites such as torrent portals, 'warez' communities and other services hosting pirated content. The Trojan is in fact a small script forcing advertisements in your browser. While some of the advertisements are related to free online games, others may expose the computer user to hardcore pornography or other types of inappropriate content.
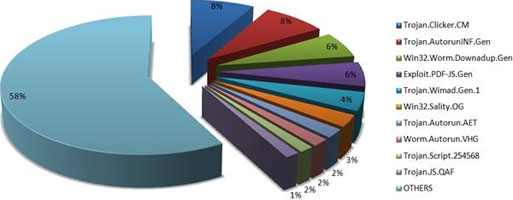
With a percentage of 8,17, the second e-threat is Trojan.AutorunInf.Gen, a generic mechanism to spread malware using removable devices such as flash drives, memory cards or external hard-disk drives. For instance, Win32.Worm.Downadup and Worm.Zimuse are two of the most famous families of malware to use this approach to infect other systems. So, great attention should be paid to the use of such external devices: they may be an easy solution when it comes to data transportation, but they might easily harm the computer if used carelessly. Libraries, copy shops and other public hotspots are usually the most notorious sources of infection.
Ranking third, Win32.Worm.Downadup.Gen is responsible for 6,18% of the global infections. Exploiting the Microsoft Windows Server Service RPC Handling Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (MS08-67), this worm spreads on other computers in the local network and restricts users’ access to Windows Update and security vendors’ web pages. Newer variants of the worm also install rogue antivirus applications, among others. The worm’s persistence after more than one year since its original appearance reveals that most users are reluctant to updating both the operating system and their locally-installed antimalware solution.
BitDefender’s fourth e-threat is Exploit.PDF-JS.Gen, with 5,76% of the total amount of infections. This generic detection deals with malformed PDF files exploiting different vulnerabilities found in Adobe PDF Reader's Javascript engine in order to execute malicious code on users’ computer. Upon opening an infected PDF file, a specially crafted Javascript code triggers the download and automatic execution of malicious binaries from remote locations.
Ranking fifth with 4,30% of the global infections, Trojan.Wimad.Gen.1 is mostly found on Torrent websites disguised as an episode of your favorite series that has not been aired yet. These fake video files are able to connect to a specific URL and download malware posing as the appropriate codec required for playing the file. Trojan.Wimad.Gen.1 is particularly active when box-office titles are expected to appear on file-sharing websites.
The sixth place with 2,73% of the infections triggered globally is taken by Win32.Sality.OG. This malicious e-threat is a polymorphic file infector that appends its encrypted code to executable files (.exe and .scr binaries). The Sality family is extremely difficult to detect and annihilate because these viruses constantly change their code, while the rootkit component tries to disable various antivirus applications installed on the infected system.
Trojan.Autorun.AET, a malicious code spreading via the Windows shared folders, as well as through removable storage devices, ranks seventh with 2,01% of the worldwide infections. The Trojan exploits the Autorun feature implemented in Windows operating systems prior to Vista SP2 for automatically launching applications when an infected storage device is plugged in. Given the potentially harmful side effects of the Autorun feature, Microsoft decided to disable it in Windows Vista SP2 and Windows 7.
Worm.Autorun.VHG is an Internet/network worm that exploits the Windows MS08-067 vulnerability in order to execute itself remotely using a specially crafted RPC (remote procedure call) package (an approach also used by Win32.Worm.Downadup). The worm ranks eighth with 1,69% of the global infections.
Trojan.Script.254568 ranks ninth with 1,40% of the global malware detection in January. This heavily-encrypted JavaScript code looks for a cookie file called 'CoreBeta'; if the cookie is not on the computer, then it will be created and set to expire in a day. The cookie’s presence signals the Trojan that the system had already been infected. If the script finds the cookie, then it would inject some masked components in various webpages, while other web resources will be hijacked to 'about:blank' pages.
With 1,40%, Trojan.JS.QAF is tenth in Top Ten e-threats. This highly obfuscated Java Script is hard to be read, making its detection quite difficult. Trojan.JS.QAF creates an 'IFrame' that redirects the users.

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.