

Metrological effects of fog and rain on IR camera performance.
Thermal cameras have the ability of producing a crisp clear thermal image of the scene in total darkness. They do not need any light at all and the smallest of details can be seen without any illumination. Therefore, it is an excellent instrument for numerous night vision applications.
A question asked very frequently is: "What happens to the range in fog, rain or any other climatical condition?" The answer would simply be, that although thermal technology is one of the best means of viewing a scene when there is rain, smoke, fog or even snow, the distance we can see is affected by these atmospheric conditions, but how much?
Transmittance of infrared radiation
Even in clear skies, inherent atmospheric absorption places limits on how far a particular infrared camera can see. A thermal imaging camera produces an image based on the differences in thermal radiation that an object emits. In essence, the farther this infrared signal has to travel from the target to the camera detector, the more of that signal can be lost along the way.
As such, the attenuation factor needs to be taken into account. This is the ratio of the incident radiation to the radiation transmitted through a shielding material. Humid air acts as a shield for infrared radiation. Summer month atmospheres usually have a higher attenuation compared to winter months due to increased humidity levels. Therefore, assuming you have clear skies and good weather conditions, you will be able to see farther with a thermal imaging camera in winter than in summer.
Humid air is only one example of how infrared radiation can be lost. Fog and rain can severely limit the range of a thermal imaging system due to scattering in the droplets of water. The higher the density of droplets, the more the infrared signal is diminished. Therefore, the next question from the customers: "How much rain and fog will limit the range performance of a thermal infrared camera and how does this compare to the range in the visible region of the spectrum?"
Fog classification
Fog is a visible aggregate of minute water droplets suspended in the atmosphere at or near the surface of the earth. Relative humidity is almost 100% when the air is almost saturated with water vapour and fog can form in the presence of a sufficient number of condensation nuclei, which can be smoke or dust particles.
There are different types of fog. Advection fog is formed through the mixing of two air masses with different temperatures and/or humidity. Radiative fog is formed in a process of radiative cooling of the air at temperatures close to the dew point.
Some of the fog banks are denser than others because the water droplets have grown bigger through accretion.
There are different ways to classify fog. An often-used classification is the one used by the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO). According to this system, fog can be classified in four categories:
* Category I: visual range 1220 metres.
* Category II: visual range 610 metres.
* Category IIIa: visual range 305 metres.
* Category IIIc: visual range 92 metres.
The reason for degradation of visibility in a foggy atmosphere is the absorption and scattering of natural or artificial illumination by fog particles. The amount of absorption and scattering depends on the microphysical structure of the fog particles, which are called aerosols.
Moderate resolution propagation model (MODTRAN)
MODTRAN is an atmospheric radiative transfer code created and supported by some military air force units. It has the ability to model the atmosphere under a variety of atmospheric conditions. It can predict atmospheric properties including path radiances, path transmissions, sky radiances and surface reaching solar and lunar irradiances for a wide range of wavelengths and spectral resolutions.
MODTRAN offers six climate models for different geographical latitudes and seasons. The model also defines six different aerosol types which can appear in each of the climates. Each of the climate models can be combined with the different aerosols.
How far you can see through fog or rain with a thermal imaging camera will also depend on the climate in which you are using the camera and the type of aerosol which is present in this specific climate.
The input data for the MODTRAN model.
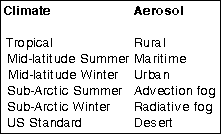
The input data for the MODTRAN model are the abovementioned specific climates and aerosols but also the visibility according to ICAO categories, geometry and length of the atmospheric path and the temperature and emissivity of the target and background.
In general, a comparison of the different aerosols shows that the maritime aerosols always result in the lowest detection range independent of the climate model, since maritime aerosols have an average greater particle radii than rural and urban aerosols. The rural and urban aerosols produce noticeable greater detection ranges in the infrared band.
This means that you can see less well through fog in maritime conditions than in land conditions, irrespective of the climate type.
Thermal imaging camera and target
Just as the type and thickness of the atmosphere has an influence on how far one can see through fog, the type of infrared camera used and specifically the waveband in which it operates are also of importance.
There are two wavebands for thermal imaging cameras: 3-5 μm (MWIR) and 8-12 μm (LWIR). The 5-8 μm band is blocked by spectral absorption of the atmosphere by water vapour to such a tremendous extent that it is rarely used for imaging.

Un-cooled thermal cameras operate in the LWIR band and cooled cameras operate in the MWIR range. The MWIR cameras are very sensitive to small temperature changes in scene temperatures, and are mainly used for long range applications.
Detection range
The conditions of the atmosphere alone are not enough to predict how far one can see through fog or rain. The size of the target and the temperature difference with the background both need to be taken into account. Furthermore, the limited spatial resolution of the optics and the detector, and the noise of the detector and signal processing also reduce the contrast radiance of target to background. The influence of the infrared sensors' transfer functions on the contrast radiance is simulated with the TACOM thermal image model (TTIM). This model enables to simulate different types of IR sensors with focal plane arrays.
Conclusion
All detection ranges for IR are significantly better than visible for Cat I type of fog. For Cat II type of fog the result is four times better with a thermal imaging camera equipped with a LWIR detector compared to visual. In Cat IIIa and Cat IIIc types of fog, there is virtually no difference between how far you can see with a thermal imaging camera and with the naked eye since the atmosphere is the limiting factor. Radiation does not penetrate through this dense type of fog in all (visible, MWIR and LWIR) spectral bands.
Just like it is impossible to give a simple answer to the question: "how far can I see with a thermal imaging camera?" it is equally impossible to say how much shorter the range will be in foggy or raining conditions. This is not only dependent on the atmospheric conditions and the type of fog but it is also dependent on the IR camera used and on the properties of the target (size, temperature difference of the target and background etc).
Acknowledgement to Flir - Technical Notes.
For more information contact Tinus Diedericks, Timeless Technologies, +27 (0)21 914 6144, tinus@timetech.co.za, www.timetech.co.za

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.