Transceiver architectures for low-cost radios - Part I
9 April 2003
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Access Control & Identity Management
Steve Moore, director applications, Micro Linear
Anyone who has ever worked in the wireless field knows there are as many different wireless implementations as there are useful applications. Many of today's systems engineers continue to have difficulty specifying detailed radio requirements and evaluating possible trade-offs in performance. At times it seems easier to just select one of the popular wireless systems that we hear about everyday (eg, 802.11, Bluetooth) and not sweat the specifics of the wireless implementation.
For applications where interoperability is a requirement this is a logical (and necessary) choice, but for many other wireless applications (eg, cordless phones, industrial control, consumer game controllers, meter reading, wireless audio, security) systems designers can usually reduce size, cost, and power by using highly-integrated RF transceivers (like the Micro Linear ML2724) and developing simple radio protocols optimised to the specific application.
For example, using an 802.11 solution running at 11 Mbps with carrier sense multiple access, full TCP/IP stack, encryption, and PCMCIA host interface for anything other than a high-speed, Ethernet-compatible wireless network will almost certainly result in unnecessary cost, size, and power. Likewise, a Bluetooth solution, while much lower cost and lower power than 802.11, still carries the additional overhead associated with a complex peer-to-peer personal area network (PAN) designed with interoperability as its primary feature.
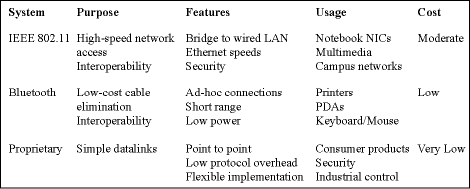
The downside of adopting standards-based solutions is that in a lot of wireless applications these solutions have many features not required resulting in unnecessary cost and power. Table 1 shows a simple comparison of the features, intended purpose, and relative cost between some of the more popular solutions.
To effectively realise an optimal wireless solution doesn't have to be complex and mysterious, especially with today's highly integrated radio transceiver ICs. Knowing basic radio specifications and how to choose a radio architecture and link protocol is all that is necessary.
Table 1. Comparison of common wireless systems
In a subsequent issue of Dataweek I will present Part II of this series that will describe some of the basic system-level radio specifications to consider along with a brief overview of common radio architectures found in today's integrated transceivers.
For more information contact Kevin Jurrius, Components & System Design, 011 979 4274.
Further reading:
Wi-Fi 6/BLE module enables rapid development
Altron Arrow
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Telit Cinterion has announced the WE310K6, a fully integrated, low-power module featuring dual-band, dual-stream Wi-Fi 6, and dual-mode Bluetooth/BLE.
Read more...
Low phase noise amplifier
RFiber Solutions
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
The MAAL-011158 from Macom is an easy-to-use low-phase noise amplifier that provides 12 dB of gain in a 32-lead QFN plastic package.
Read more...
Webinar: Enabling the digital transformation of IIoT with Bluetooth
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Key industrial use cases for Bluetooth will be reviewed, including the main performance requirements for Bluetooth in industrial applications, and the technical features available.
Read more...
Full sensor to cloud solution
CST Electronics
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
NeoCortec has demonstrated the seamless and rapid development of full sensor-to-cloud solutions using NeoMesh Click boards from MikroE and the IoTConnect cloud solution from Avnet.
Read more...
Long-range Wi-Fi HaLow module
TRX Electronics
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
One of Mouser’s newest products is the Morse Micro MM6108-MF08651-US Wi-Fi HaLow Module, which adheres to the IEEE 802.11ah standard.
Read more...
Quectel launches 3GPP NTN comms module
Quectel Wireless Solutions
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Quectel Wireless Solutions has announced the Quectel BG95-S5 3GPP non-terrestrial network (NTN) satellite communication module.
Read more...
SIMCom’s A7673x series
Otto Wireless Solutions
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
SIMCom recently released the A7673X series, a Cat.1 bis module based on the ASR1606 chipset, that supports wireless communication modes of LTE-FDD, with a maximum downlink rate of 10 Mbps and a maximum uplink rate of 5 Mbps.
Read more...
Accelerating the commercialisation of the 5G IoT markets
Altron Arrow
Editor's Choice Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Fibocom unveils Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) module MA510-GL, enabling satellite and cellular connectivity to IoT applications.
Read more...
Long-range connectivity module
Avnet Silica
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Digi XBee XR 868 RF Modules support the deployment of long-range connectivity applications, and support point-to-point and mesh networking protocols.
Read more...
4G LTE-M/NB-IoT connectivity reference design
iCorp Technologies
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Developed around the industry-leading Nordic nRF9160 module, the platform comes complete with a newly-developed LTE antenna, ATRIA, which is pre-certified to operate over the full LTE-M and NB-IoT bands.
Read more...